Working Time
-
Mon - Sat :
10:00am - 01:00pm
05:00pm - 08:00pm
Contact Info
-
Phone: 7624008000
- recombhtc@gmail.com
Female Pattern Hair Loss

What is Female Pattern Hair Loss?
Female pattern hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common form of hair loss among women. Unlike male pattern baldness, which often begins with a receding hairline, female pattern hair loss typically presents as diffuse thinning across the entire scalp. This condition is influenced primarily by genetics and hormonal changes, particularly the effects of androgens like dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which can shrink hair follicles and disrupt the normal hair growth cycle. While female pattern hair loss can start at any age, it often becomes noticeable during menopause or other periods of hormonal fluctuation.
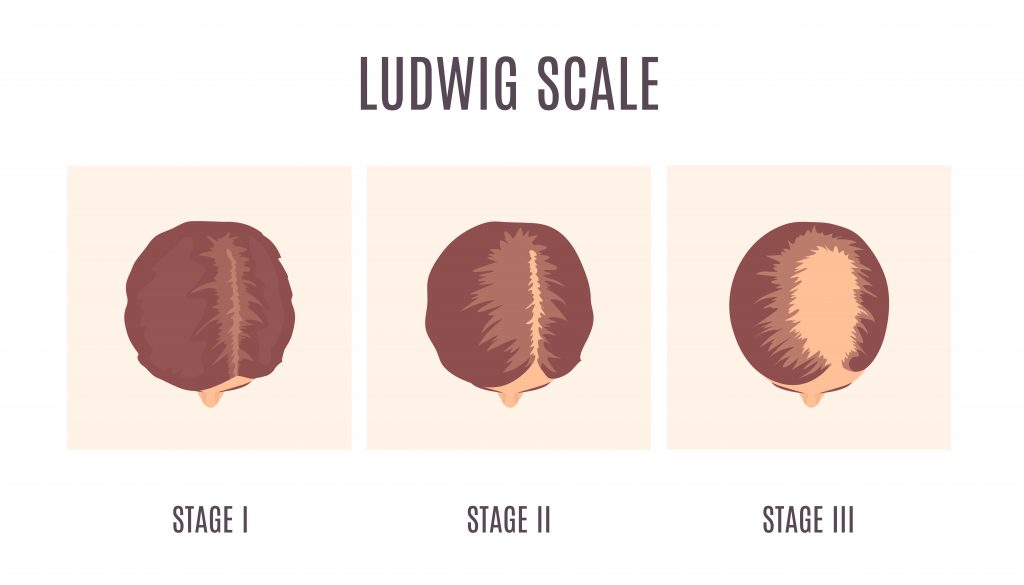
Ludwig Scale of Baldness
The Ludwig scale is a classification system specifically designed to evaluate the extent of hair loss in women. It includes three distinct stages:
- Stage 1: This stage involves a slight thinning of the hair, usually noticeable at the crown or part line, but the hair loss is not yet severe.
- Stage 2: Hair thinning becomes more pronounced and is visible across a larger portion of the scalp. The thinning is more noticeable and can be observed through a widening of the part line or overall decrease in hair density.
- Stage 3: This stage represents the most advanced form of female pattern hair loss, where thinning is significant and widespread. There is a noticeable reduction in hair volume and density throughout the scalp, with possible visibility of the underlying scalp.
Treatment Options for Female Pattern Hair Loss
Several treatment options are available for female pattern hair loss, ranging from medications and non-invasive therapies to surgical procedures and lifestyle changes:
- Medications:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This over-the-counter topical solution is approved for use in women and can help stimulate hair growth and slow hair loss. It is available in various strengths and is applied directly to the scalp.
- Spironolactone: A prescription oral medication that acts as an anti-androgen, reducing the effects of androgens on hair follicles. It can help slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
- Hormone Therapy: For hair loss related to hormonal imbalances, treatments such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or birth control pills can help stabilize hormone levels and reduce hair thinning.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): This non-invasive treatment uses low-level laser light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. It can be administered in a clinical setting or with at-home devices.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: In this procedure, a small amount of the patient’s blood is drawn, processed to concentrate platelets, and then injected into the scalp to enhance hair growth and improve hair density.
- Hair Transplantation:
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This technique involves extracting individual hair follicles from a donor area and transplanting them to areas of thinning or baldness on the scalp. FUE is minimally invasive and leaves minimal scarring.
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): This method involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dividing it into individual follicular units, and transplanting these units to thinning areas. FUT can be effective but leaves a linear scar.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients (such as iron, zinc, and vitamins A and D), managing stress, and avoiding harmful hair practices can help support overall hair health.
- Cosmetic Solutions: Wigs, hairpieces, and hair extensions can offer immediate cosmetic improvements for women experiencing significant hair loss.
Women dealing with hair loss should seek consultation with a healthcare professional or dermatologist to identify the most appropriate treatment options based on their individual condition and health status.


